Wearable Health Monitors: The Future of Personalized Healthcare and Fitness
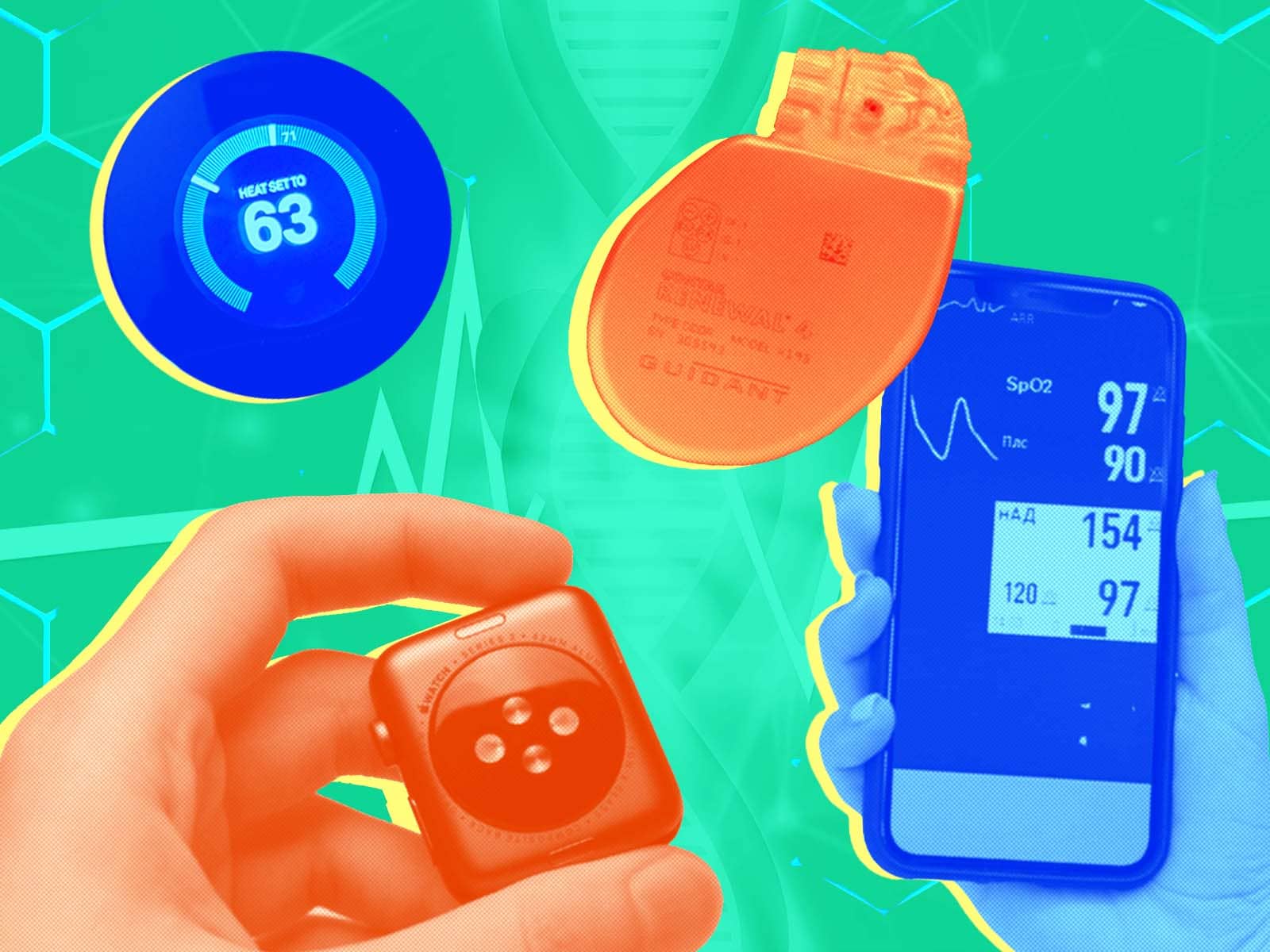
Wearable health monitors are transforming healthcare by providing continuous, real-time tracking of vital health metrics. These devices range from fitness trackers to advanced medical-grade monitors, offering insights into users’ physical activity, heart rate, sleep patterns, and more. Here’s an overview of the current landscape of wearable health monitors, their benefits, and emerging technologies that are shaping personalized healthcare.
1. Types of Wearable Health Monitors
Wearable health monitors come in various forms, offering a wide range of functions tailored to users’ health needs:
Fitness Trackers
- Examples: Fitbit, Garmin, Xiaomi Mi Band
- Functions: Track steps, calories burned, heart rate, and sleep patterns.
- Benefits: Useful for general fitness and wellness, these devices encourage users to maintain an active lifestyle by providing data on daily activities.
Smartwatches
- Examples: Apple Watch, Samsung Galaxy Watch
- Functions: In addition to fitness tracking, smartwatches monitor heart rate, oxygen saturation (SpO2), and can even perform electrocardiograms (ECGs).
- Benefits: Smartwatches provide broader functionality, including notifications, apps, and advanced health tracking features, such as detecting irregular heart rhythms and falls .
Medical-Grade Wearables
- Examples: Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs), cardiac monitors like Zio by iRhythm.
- Functions: Track specific health metrics like glucose levels or heart rhythms over long periods.
- Benefits: These devices are often prescribed by healthcare professionals for patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or arrhythmia, allowing for better disease management(Smithsonian Magazine)(CAS).
2. Key Features and Functions
1. Heart Rate Monitoring
Most wearable devices offer continuous heart rate monitoring, which is useful for assessing overall cardiovascular health. Advanced features like ECG capabilities in devices like the Apple Watch enable early detection of atrial fibrillation(AFib), which is linked to stroke and heart failure(World Economic Forum).
2. Blood Oxygen Saturation (SpO2)
Devices with SpO2 monitoring provide real-time data on blood oxygen levels, a crucial metric during the COVID-19 pandemic as low oxygen levels can indicate respiratory issues. This feature is now commonly found in smartwatches like the Apple Watch Series 6 and Garmin Fenix series .
3. Sleep Tracking
Advanced wearables analyze sleep stages—light, deep, and REM—providing insights into sleep quality. Poor sleep is linked to various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, obesity, and diabetes. Devices like Fitbit and Whoop excel in offering detailed sleep metrics and recommendations .
4. Continuous Glucose Monitoring
For diabetic patients, Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) like the Dexcom G6 or Freestyle Libre continuously track blood glucose levels without the need for fingerstick tests. These devices alert users when blood glucose levels are too high or low, helping manage diabetes more effectively .
3. Emerging Technologies and Trends
Wearable Biosensors
The future of wearable health monitors lies in biosensor technology, which enables continuous tracking of more advanced biomarkers, including stress levels, hydration, and lactate for athletes. Companies like Biostrap and Ava are exploring multisensor platforms that monitor various physiological metrics in real-time.
Smart Textiles
Another promising development is smart textiles, where sensors are embedded into clothing to monitor vitals like heart rate and temperature. These could be particularly useful in healthcare settings for patients needing constant monitoring .
AI and Predictive Analytics
Wearables are integrating AI to provide predictive health insights, which can forecast potential health issues before they arise. For example, AI algorithms can analyze heart rate variability (HRV) to predict stress or risk of heart conditions. Companies like WHOOP are already using this technology to help athletes optimize recovery and performance .
4. Benefits of Wearable Health Monitors
1. Early Disease Detection
Wearable health monitors allow for the early detection of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and sleep apnea. By continuously tracking health metrics, these devices can alert users or healthcare providers to anomalies, prompting early intervention.
2. Personalized Health Insights
Wearables provide users with data tailored to their specific health goals. For example, someone looking to lose weight can track their caloric expenditure and adjust their diet accordingly. Those managing chronic conditions can better understand how lifestyle choices affect their health.
3. Improved Healthcare Access
Wearable monitors reduce the need for frequent in-person doctor visits by providing continuous data that healthcare providers can access remotely. This is especially beneficial for patients in rural areas or those with mobility issues .
4. Enhanced Fitness and Wellness
For fitness enthusiasts, wearables provide real-time feedback on workouts, helping users optimize performance and recovery. Devices like Garmin and Whoop offer insights on strain, sleep, and recovery, making them popular among athletes.
5. Challenges and Considerations
Accuracy
While wearables provide a wealth of data, concerns remain about the accuracy of certain metrics. For example, some studies suggest that fitness trackers may not accurately measure calories burned during exercise. Continuous improvement of sensor technology is critical for making wearables reliable for clinical use .
Privacy and Data Security
With wearable devices collecting sensitive health data, privacy and security are major concerns. Companies must ensure that user data is encrypted and that robust privacy policies are in place to protect against breaches .
Conclusion
Wearable health monitors are transforming healthcare by empowering users with real-time health data, promoting early disease detection, and improving access to personalized care. As sensor technology advances and AI becomes more integrated, wearables will continue to play a significant role in both individual wellness and the broader healthcare landscape. From fitness enthusiasts to chronic disease patients, wearable health monitors are becoming an essential tool in proactive health management.
References:
- CNET: “Best Wearable Health Devices”
- Harvard Health: “How Wearables Are Changing Health”
- Nature: “Wearable Biosensors”